Service Description:
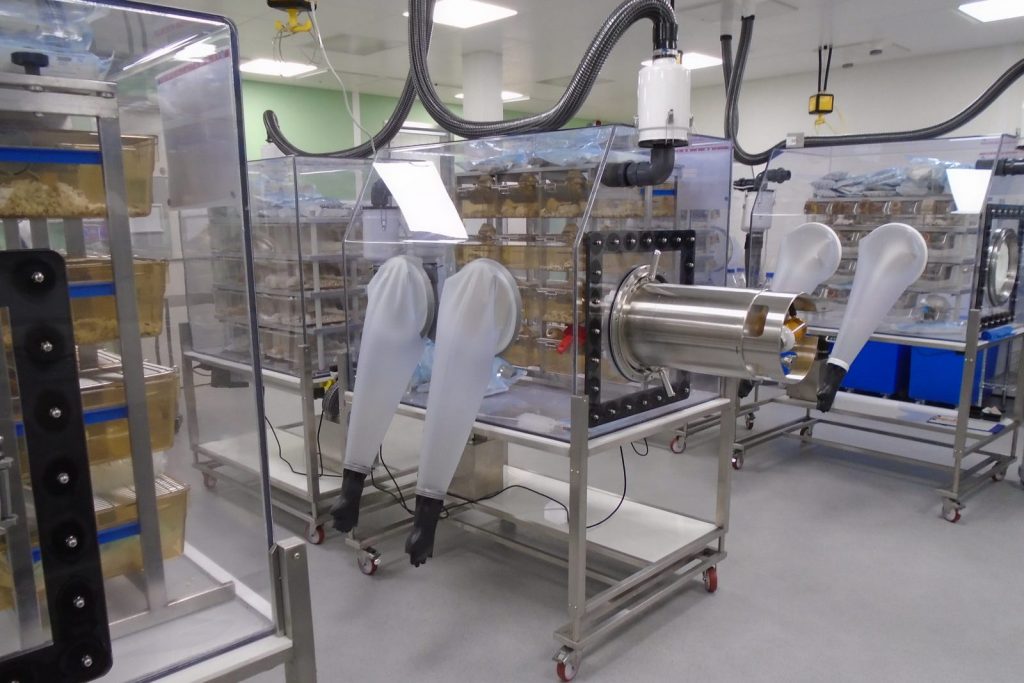
In the Axenic/Gnoto Facility at the Gulbenkian Institute for Molecular Medicine (GIMM), several specific techniques have been validated in the facility: body weight and body temperature measurement, buccal swab, IP and IV injections, gavage, blood collection, feces collection, surgeries (vasectomy, and renal ischemia-reperfusion), OGTT (Glucose tolerance), ITT (Insulin tolerance), and solid tumour size measurement and follow-up.
Like other research facilities at the GIMM, the Axenic / Gnoto Facility is available to scientists worldwide. Researchers who want to work with these mice can be temporarily hosted at the Institute’s laboratories if they wish to conduct their own experiments on site.