-
Ghorbanalipoor S, Hommel T, Kolbe T, et al. The loss of keratin 77 in murine skin is functionally compensated by keratin 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024; Nov 25:119881. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119881
-
Hedegger K, Blutke A, Hommel T, et al. Trapping all ERBB ligands decreases pancreatic lesions in a murine model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Oncol. 2023; Nov;17(11):2415-2431. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13473
-
Hedegger K, Algül H, Lesina M, et al. Unraveling ERBB network dynamics upon betacellulin signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. *Mol Oncol. 2020;Aug;14(8):1653-1669. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12699
Service Description:
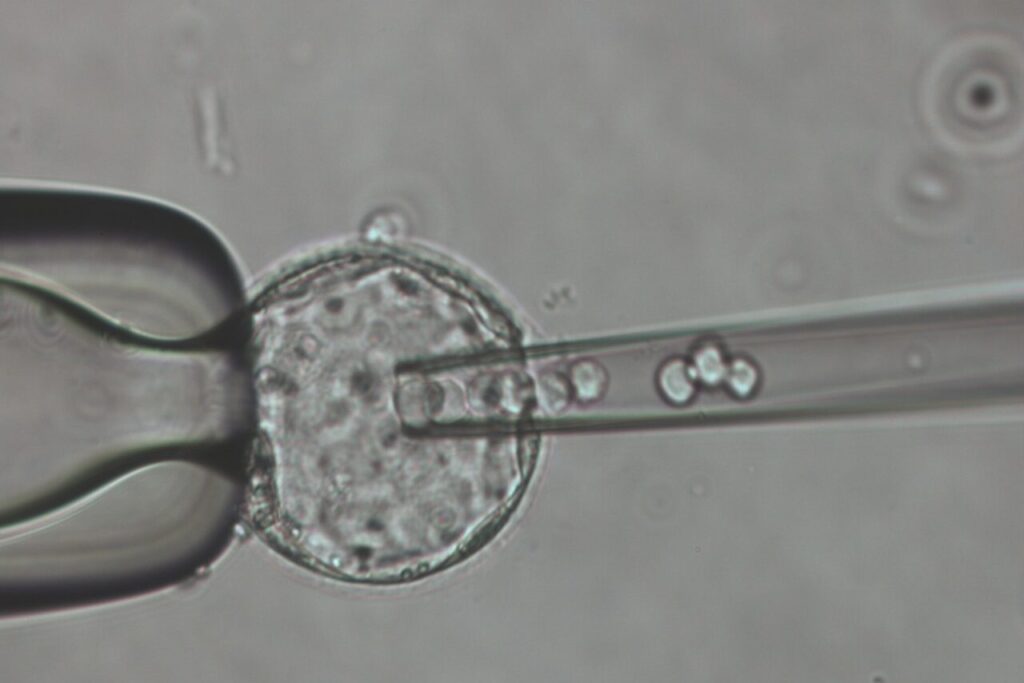
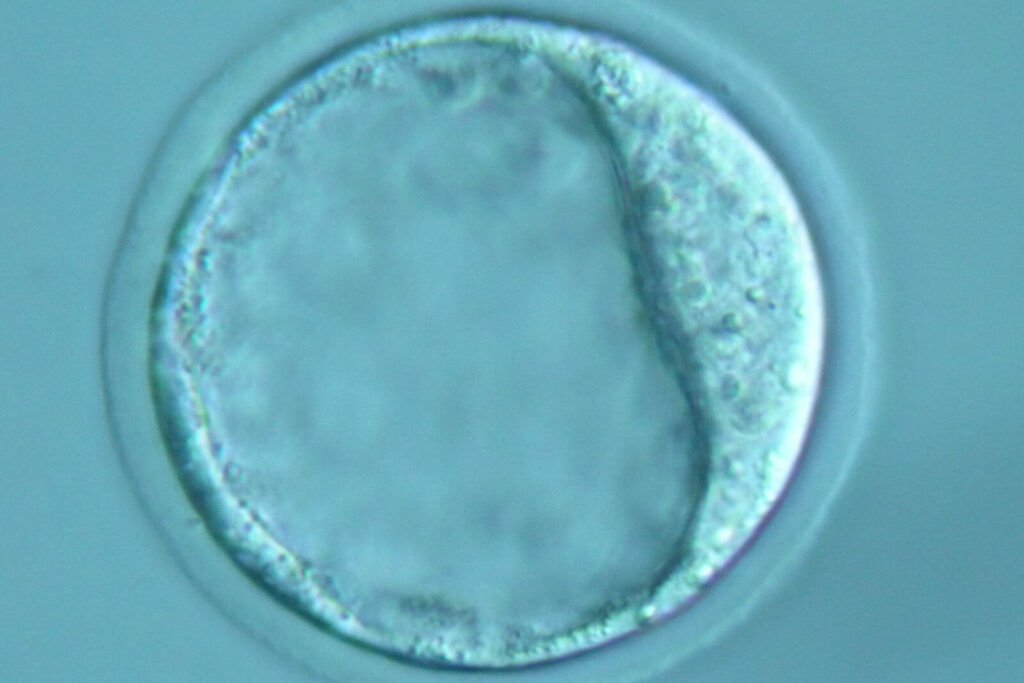
The University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna (Vetmeduni) offers the generation of novel genetically modified mouse lines using DNA microinjection, ES cell injection, e.g. for the generation of new knockout or knock-in mouse models. The service can include the design and generation of DNA micro fragments or ES cells. Mouse models could also be generated by using CRISPR/Cas9 technology that enables the modification of genome to produce precise and unique genetically modified mouse models. The service includes the design of guides and DNA template, preparation, and electroporation of the targeting complex into zygotes to generate F0 founder mutant animals (C57BL/6 genetic background preferred). Vetmeduni always try to minimise the off-target effects and increase the on-target effects of the guide RNAs. Selected F0 animals will be bred to germline to produce F1 genome edited animals. Possible allele types that can be generated are indels, exon deletions (< 5kb), point mutations, and small insertions. Newly developed mouse models will be made available to selected applicants within an average of 12 months following provision of all required information to start the mouse production. Novel models are archived as cryopreserved material and distributed as part of the EMMA archive. The price is calculated individually and depends on the scope of the service required for the generation of the desired mouse line.